|
Circular foundations |

|

|
Circular foundations
In the case where the foundation is subject to axial action and moment around one or two axes, as shown in the image below, in the calculation of the bearing capacity must be considered the effect produced by the eccentricity of the loads using equivalent dimensions of the foundation (B', L'), ie the minimum reduced surface area with respect to which the resultant is centered.
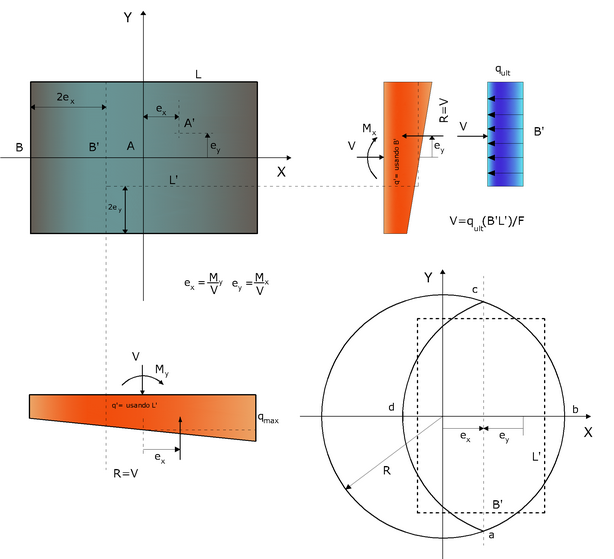
Method of calculating the equivalent size of a foundation subjected to not barycentric load
The two analyzed cases are:
| • | Square or rectangular foundations |
![]()
for which the equivalent area is Af=B'L'
| • | Circular foundations |
The effective area of a circular foundation can be calculated by taking ex on a generic axis (in our case the X axis) and calculating the area of the zone abcd subject to centered load.
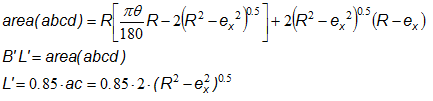
From previous relationships we obtain B', in the particular case ex = 0, the equivalent surface coincides with the rectangle inscribed in the circumference, in the case where ex = R the bearing capacity is almost nil.
© GeoStru Software